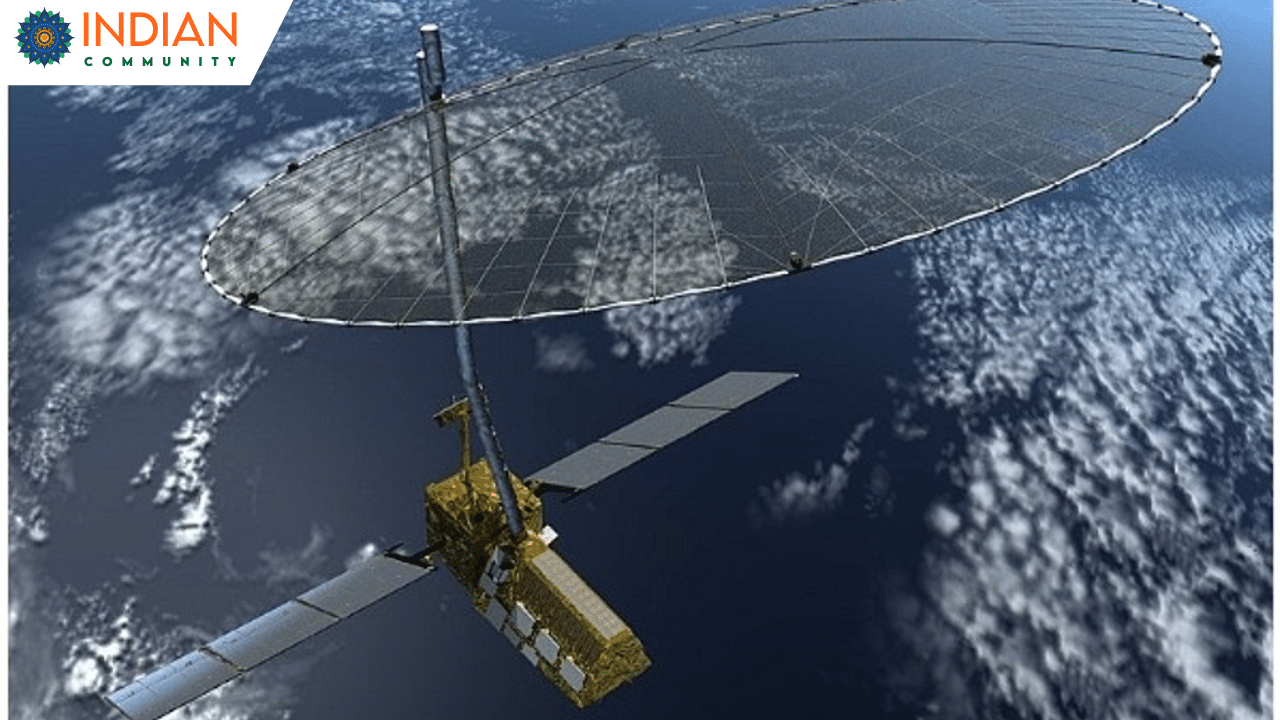
The upcoming NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) mission represents a significant collaboration between the United States and India, aiming to provide unprecedented insights into Earth’s ever-changing surface. Scheduled for launch from India, NISAR is poised to revolutionize our understanding of natural hazards, climate change, and ecosystem dynamics.
Mission Overview
NISAR is a joint venture between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), marking the first time the two agencies have cooperated on hardware development for an Earth-observing mission. The satellite is equipped with advanced dual-band radar systems—L-band and S-band—that enable it to detect subtle changes in Earth’s surface, capturing data with remarkable precision.
Technological Innovations
The satellite’s dual-band radar operates at different wavelengths: the L-band with a 10-inch (25-centimeter) wavelength and the S-band with a 4-inch (10-centimeter) wavelength. This configuration allows NISAR to interact with various Earth features differently, enhancing its ability to monitor a wide range of phenomena. Shorter wavelengths are more sensitive to smaller objects like leaves and rough surfaces, while longer wavelengths interact more with larger structures like tree trunks and boulders. By utilizing both radar systems, NISAR provides a more comprehensive understanding of Earth’s surface changes.
Scientific and Practical Applications
NISAR’s capabilities are vast, including:
Natural Hazard Monitoring: The satellite will track land deformation caused by earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic activities, providing critical data for disaster preparedness and response.
Climate Change Assessment: NISAR will observe the effects of climate change on glaciers, ice sheets, and forests, offering insights into the global carbon cycle and contributing to climate change mitigation strategies.
Agricultural Management: By monitoring soil moisture levels and crop conditions, NISAR will support sustainable agricultural practices and food security efforts.
Infrastructure Monitoring: The mission’s high-resolution data can detect ground subsidence and infrastructure stability, aiding urban planning and hazard mitigation.
Global Collaboration and Data Accessibility
The NISAR mission exemplifies international cooperation, with hardware components built across different continents and assembled in India. NASA is committed to making NISAR’s data freely accessible by processing and storing it in the cloud, ensuring that users worldwide can utilize the information for various purposes, from scientific research to disaster response.